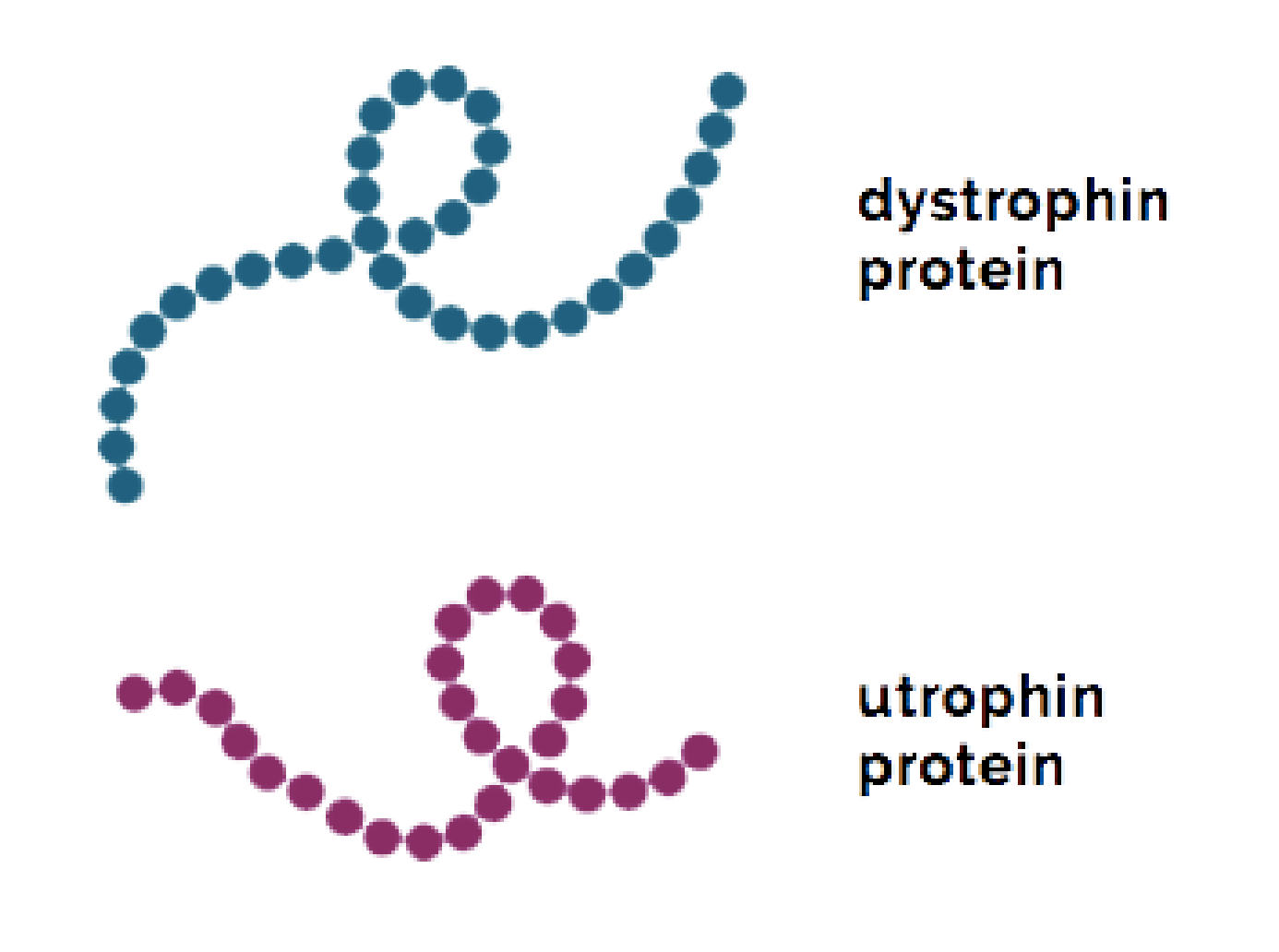Research Approaches That Aim to Promote Muscle Growth or Protect Muscle
These 4 potential new therapies are being developed to stimulate muscle growth and/or protect existing muscle.
Antifibrotic Therapies
As muscles weaken and are damaged in DMD, a process called fibrosis takes place. Fibrosis is similar to scarring and causes muscle fibers to be replaced by fat and connective tissue. This prevents muscles from working properly. Researchers are currently conducting clinical trials to determine whether these muscle fibers can be protected by medications that target the fibrosis process.1
Myostatin Inhibition
Myostatin is a protein that regulates muscle growth to prevent muscular hypertrophy. In patients with DMD, the action of myostatin can contribute to muscle wasting. The goal of myostatin inhibition therapies is to promote muscle regeneration and slow disease progression.1
Utrophin Stimulation
Utrophin, also known as dystrophin-related protein, has many of the same structural and protein-binding functions of dystrophin. Utrophin expression is typically downregulated after early development in favor of dystrophin. However, in patients with DMD, increasing the production of utrophin may help compensate for the lack of dystrophin, potentially preventing muscle degeneration.1
Stem Cell Approaches
In the absence of dystrophin, DMD patients experience progressive muscle wasting that eventually exceeds the capacity of muscles to regenerate. Stem cell therapies are currently under investigation that aim to restore a healthy population of muscle stem cells that is capable of self-renewal and regeneration. These therapies may use cells derived from the patient that are then genetically altered outside of the body to restore dystrophin production or use cells obtained from a healthy individual expressing dystrophin.2